Networks Virtualization
Beyond the technology, we see Network virtualisation as a key trend that will impact the organisation of the operators and service providers. Maximising the benefit of network virtualisation means reviewing all operational process. Relations between business, IT and networks will dramatically change.
Definition from SDN central -
Network virtualization (NV) creates logical, virtual networks that are decoupled from the underlying network hardware to ensure the network can better integrate with and support increasingly virtual environments. Over the past decade, organizations have been adopting virtualization technologies at an accelerated rate.
With virtualization, companies can take advantage of the efficiencies and agility of software-based compute and storage resources. While networks have been moving towards greater virtualization, it is only recently, with the true decoupling of the control and forwarding planes, as advocated by software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV), that network virtualization has become more of a focus.
8/01/2015
As NFV and SDN are getting more and more attention and credibility from telecom industry, I see huge opportunities for :
- telecom operators in emergent countries. Indeed, they are facing a lack of expertises in all technical domains from engineering to operations. Automation of service delivery, scalability of infrastructure with right management applications (provisionning, monitoring, reporting) can ease introduction of new services in such countries. More other, vendors of NFV/SDN solutions will have the opportunity to propose attractive pricing scheme with lower entry cost to facilitate the take off of telecom services in these countries. As financial risks will be reduced for new services, executives will take business risks easier.
- OTT player. As the entry cost should be lower, and most of operations could managed remotely and centrally, NFV/SDN could definitively help them to launch their own network (full MVNO or FVNO) in targetted countries. Strating from scratch, they would not suffer from some legacy systems and organisations requiring lots of change management to cope with the new NFV/SDN paradigm.
8/01/2015
NFV/SDN is promising lower cost, more flexibility in ressource management and in service development and automisation of service ordering. Even if the maturity of these technology is not there yet to allow large deployements, traditional and large telcos are already facing huge challenges to introduce NFV/SDN :
- IT & networks teams have to work closer in designing, deploying and operating new services.
- Relations with marketing teams and development process have to be revisited. Service delivery teams have to rethink their process and the organisation.
- For large operators or service providers, the breakout of activities between local teams (in regions) and central teams must be revisited.
- For telecom operators having outsourced part of their technical activities (network, IT or both), outsoucing contracts have to be revisited to tke incount this shift in technology. The border line between network and IT are moving.
26/11/2014
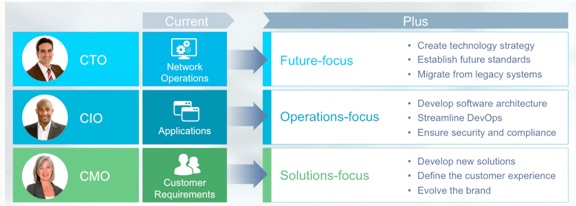
Webinar "SDN & NFV: Transforming the Service Provider Organisation". Juniper expert, Jack barret presented his view on the impact of NFV/SDN on the organisation os service provider.